Yujing Sun
Research Assitant Professor
Department of Computer Science
The University of Hong Kong
E-mail: yjsun at cs dot hku dot hk
About
I am currently a research assistant professor at the University of Hong Kong. Before that, I was a postdoctoral fellow, collaborating with Prof. Siu Ming Yiu. I obtained my PhD degree from the department of computer science, the University of Hong Kong, under supervision by Prof. Wenping Wang, in 2018, and my bachelor degree from the college of science and engineering, University of Minnesota, Twin Cities in 2013. My research covers topics in intelligent Fintech, computer graphics and image processing.Publications
Notice that most, if not all, of the final versions of these papers are copyrighted. Use these preprints at your own risk.
Understanding deep face anti-spoofing: from the perspective of data
[Paper]
Face biometrics systems are increasingly used by many business applications, which can be vulnerable to malicious attacks, leading to serious consequences. How to effectively detect spoofing faces is a critical problem. Traditional methods rely on handcraft features to distinguish real faces from fraud ones, but it is difficult for feature descriptors to handle all attack variations. More recently, in order to overcome the limitation of traditional methods, newly emerging CNN-based approaches were proposed, most of which, if not all, carefully design different network architectures. To make CNN-related approaches effective, data and learning strategies are both indispensable. In this paper, instead of focusing on network design, we explore more from the perspective of data. We present that appropriate nonlinear adjustment and hair geometry can amplify the contrast between real faces and attacks.
BitVis: An interactive visualization system for bitcoin accounts analysis
[Paper]
As an emerging payment method, bitcoin is receiving growing popularity for the different characteristics it shares with conventional fiat currencies. But the pseudonymous nature of bitcoin brings difficulties for regulators to effectively monitor bitcoin-related financial crimes. In this paper, we present an interactive system to visualize the relationship between bitcoin accounts, namely BitVis. With BitVis, users can easily filter transactions on demand, interact with the transaction networks to look for useful information, and analyze behavior of bitcoin accounts. Via BitVis, financial regulators can conveniently track suspicious accounts, while personal investors can easily investigate the activities of an interested account.
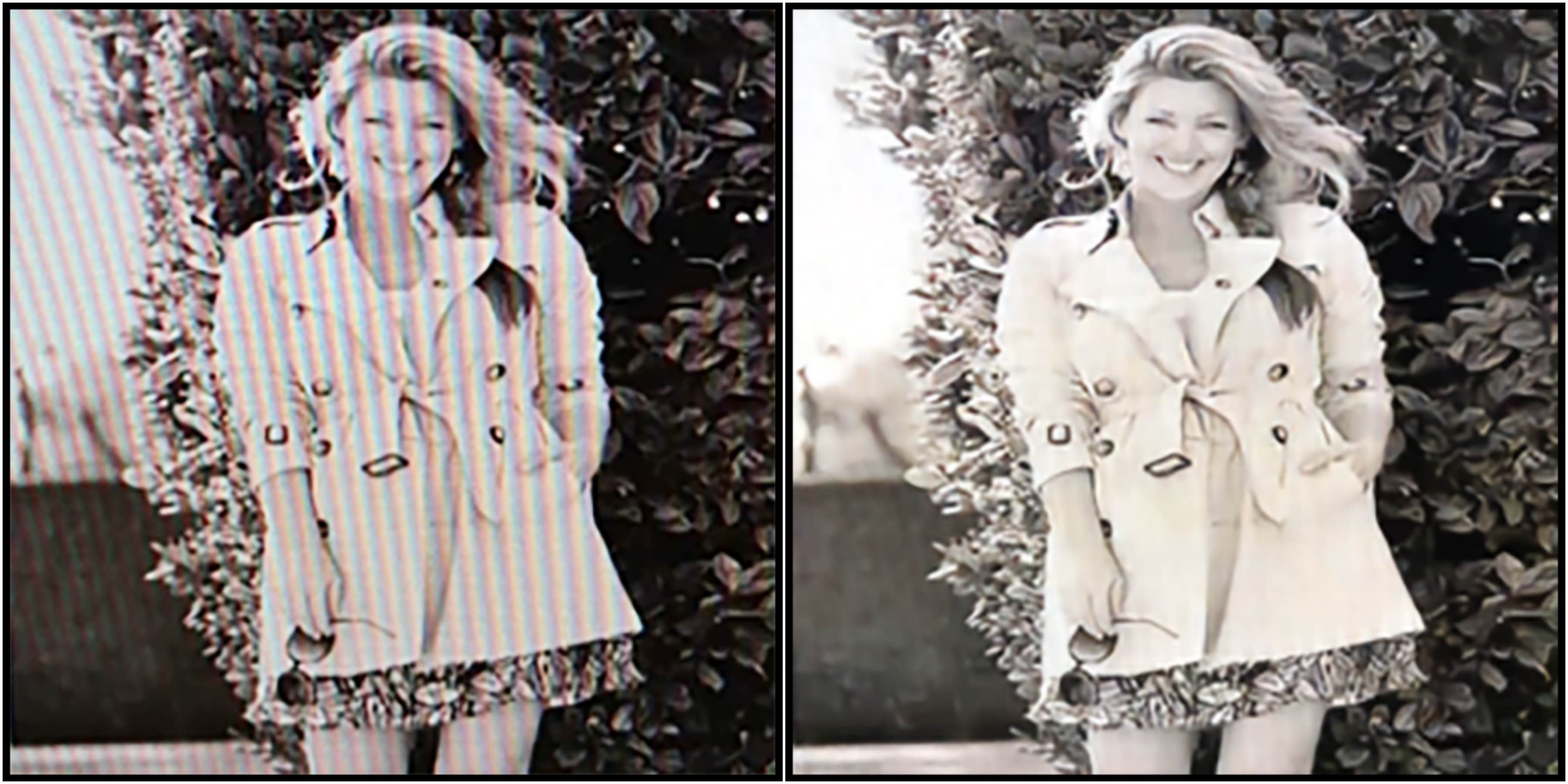

Moire Photo Restoration Using Multiresolution Convolutional Neural Networks
[Paper] [Supplemental Material] [benchmark]
Abstract: Digital cameras and mobile phones enable us to conveniently record precious moments. While digital image quality is constantly being improved, taking high-quality photos of digital screens still remains challenging because the photos are often contaminated with moire patterns, a result of the interference between the pixel grids of the camera sensor and the device screen. Moire patterns can severely damage the visual quality of photos. However, few studies have aimed to solve this problem. In this paper, we introduce a novel multiresolution fully convolutional network for automatically removing moire patterns from photos. We also create a large-scale benchmark dataset with 100,000+ image pairs for investigating and evaluating moire pattern removal algorithms. Our network achieves state-of-the-art performance on this dataset in comparison to existing learning architectures for image restoration problems.

Image Structure Retrieval via L0 Minimization
[Paper]
Abstract: Retrieving salient structure from textured images is an important but difficult problem in computer vision because texture, which can be irregular, anisotropic, non-uniform and complex, shares many of the same properties as structure. Observing that salient structure in a textured image should be piece-wise smooth, we present a method to retrieve such structures using an L0 minimization of a modified form of the relative total variation metric. Thanks to the characteristics shared by texture and small structures, our method is effective at retrieving structure based on scale as well. Our method outperforms state-of-art methods in texture removal as well as scale-space filtering. We also demonstrate our method’s ability in other applications such as edge detection, clip art compression artifact removal, and inverse half-toning.
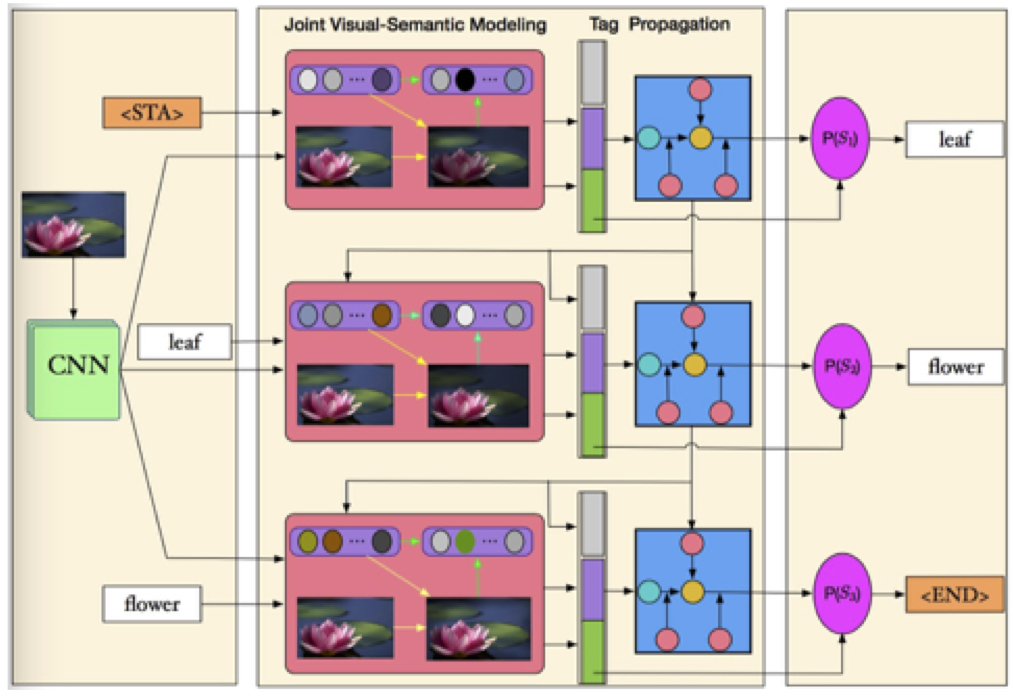
Image Tagging by Joint Deep Visual-Semantic Propagation
[Paper]
Abstract: Image tagging has attracted much research interest due to its wide applications. Many existing methods have gained impressive results, however, they have two main limitations: 1) only focus on tagging im- ages, but ignore the tags’ influences on visual feature modeling. 2) model the tag correlation without considering visual contents of image. In this paper, we propose a joint visual-semantic propagation model (JVSP) to address these two issues. First, we leverage a joint visual-semantic modeling to harvest integrated features which can accurately reflect the relationship between tags and image regions. Second, we introduce a visual-guided LSTM to capture the co-occurrence relation of the tags. Third, we also design a diversity loss to enforce that our model learns to focus on different regions. Experimental results on three challenging datasets demonstrate that our proposed method leads to significant per- formance gains over existing methods.

Denoising Point Set via L0 Minimization
[Paper]
Abstract: We present an anisotropic point cloud denoising method using L0 minimization. The L0 norm directly measures the sparsity of a solution, and we observe that many common objects can be defined as piece-wise smooth surfaces with a small number of features. Hence, we demonstrate how to apply an L0 optimization directly to point clouds, which produces sparser solutions and sharper surfaces than either the L1 or L2 norms. Our method can faithfully recover sharp features while at the same time smoothing the remaining regions even in the presence of large amounts of noise.
Professional Activities
-
Reviewer:
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing